Experience using heaters
Heating Capacity for Your Room: Calculate & Choose the Right Heater
Heating Capacity for Your Room: Calculate & Choose the Right Heater. In today’s article, cuahangxe.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding Heating Capacity and Room Size
Heating capacity is measured in BTUs, or British Thermal Units. BTUs are a measurement of heat energy. Basically, the higher the BTU rating of a heater, the more heat it can produce. To determine the heating capacity you need for your room, you need to consider the room size, insulation level, window area, ceiling height, and number of occupants.
Room Size:
The first step is to calculate the volume of your room. This is done by multiplying the length, width, and height of the room. For example, a room that is 10 feet long, 12 feet wide, and 8 feet high would have a volume of 960 cubic feet (10 x 12 x 8 = 960). The larger the room, the more heat it will require to reach a comfortable temperature.
Heat Loss Factors:
Heat loss is the amount of heat that escapes from a room. There are several factors that can contribute to heat loss, including:
- Insulation: Insulation helps to prevent heat from escaping through walls, ceilings, and floors. The higher the R-value of the insulation, the better it will insulate your room. A poorly insulated room will require a higher heating capacity to stay warm.
- Windows: Windows are a major source of heat loss. Double-pane windows are more energy-efficient than single-pane windows. Larger windows will also lead to more heat loss than smaller windows.
- Climate: The climate you live in will also play a role in determining your heating needs. Colder climates will require a higher heating capacity than warmer climates.
- Ceiling Height: Higher ceilings allow for more heat to escape. Rooms with higher ceilings will require a higher heating capacity than rooms with lower ceilings.
- Occupants: People generate heat. If you have a large number of occupants in a room, you’ll need a higher heating capacity to keep the room warm.
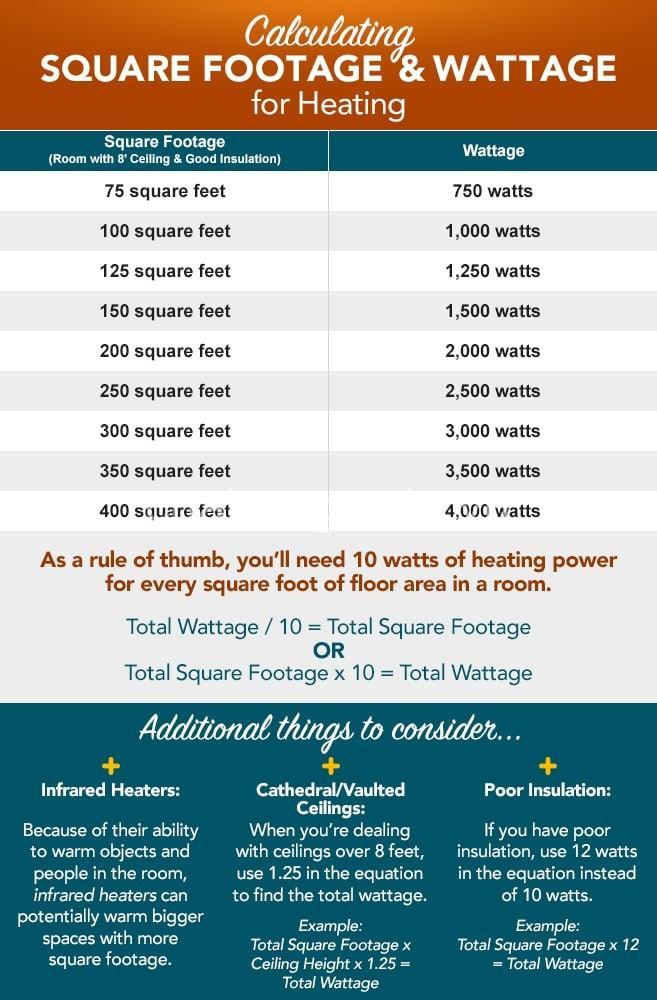
Calculating Your Heating Capacity Needs
Now that you understand the factors that affect heating capacity, let’s talk about how to calculate your needs.
Simplified Calculation:
A simple method for calculating heating capacity is to use the square footage of your room and your climate zone. You can find a chart online that shows the recommended BTU output for each climate zone.
Example:
- If you live in a climate zone 5 and your room is 150 square feet, you would need a heater with a BTU output of approximately 5,000 BTUs.
Detailed Calculation:
A more comprehensive method for calculating heating capacity takes into account all the factors mentioned above. You can use the following formula:
Heating Capacity (BTU) = Room Volume (cubic feet) x Heat Loss Factor
Heat Loss Factor:
The heat loss factor can be calculated using the following table:
| Factor | Value |
|---|---|
| Insulation (R-value) | 0.05 – 0.10 |
| Windows | 0.20 – 0.30 |
| Climate (Zone 1-5) | 0.10 – 0.20 |
| Ceiling Height (ft) | 0.05 – 0.10 |
| Occupants | 0.05 – 0.10 |
Example:
- Room Volume = 960 cubic feet
- Insulation (R-value 13) = 0.07
- Windows (double-pane) = 0.25
- Climate (Zone 5) = 0.15
- Ceiling Height (8 feet) = 0.08
- Occupants (2) = 0.08
Heat Loss Factor = 0.07 + 0.25 + 0.15 + 0.08 + 0.08 = 0.63
Heating Capacity (BTU) = 960 x 0.63 = 604.8 BTUs
Therefore, you would need a heater with a BTU output of approximately 6,050 BTUs for this room.
Online Calculators:
There are many online calculators available that can help you determine your heating capacity needs. These calculators are easy to use and can save you time and effort. You can find these calculators by searching for “heating capacity calculator” online.
Choosing the Right Heater for Your Needs
Once you know the heating capacity you need, you can start shopping for a heater.
Types of Heaters:
- Space Heaters: Space heaters are portable and can be used to heat individual rooms. They are typically less expensive than central heating systems, but they are not as efficient.
- Central Heating Systems: Central heating systems heat your entire home. They are more efficient than space heaters, but they are also more expensive to install.
Matching Heating Capacity:
When choosing a heater, make sure to select one that has a BTU output that matches your calculated heating needs. If you choose a heater that is too small, it won’t be able to heat your room effectively. If you choose a heater that is too large, it will waste energy and money.
Additional Tips for Energy Efficiency and Comfort:
- Proper Insulation: Insulation is essential for reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. Make sure your walls, ceilings, and floors are properly insulated.
- Air Sealing: Seal any air leaks around windows and doors to prevent drafts. You can use weather stripping or caulk to seal these leaks.
- Thermostat Settings: Use a programmable thermostat to optimize your heating schedule. You can set the thermostat to lower the temperature at night and when you’re away from home.
- Drafts and Cold Spots: Identify and address any drafts or cold spots in your room. This can be done by adding curtains, rugs, or draft stoppers.
Seeking Professional Advice
If you’re unsure about your heating capacity needs or if you have a complex situation, it’s best to consult with a qualified HVAC professional. They can accurately assess your heating needs and recommend the best solutions.
FAQs
What factors influence heating capacity needs?
Several factors can influence heating capacity needs, including room size, insulation level, window area, ceiling height, and the number of occupants.
What are the different types of heaters available?
Common types of heaters include space heaters, central heating systems, and heat pumps.
How do I choose the right heater for my room size?
First, calculate the heating capacity you need based on the room’s volume and heat loss factors. Then, choose a heater with a BTU output that matches your calculated needs.
What is the best way to save energy when heating my home?
To save energy, make sure your home is well-insulated, seal air leaks, use a programmable thermostat, and avoid drafts and cold spots.
What is the difference between BTU and Watts?
BTU (British Thermal Units) is the standard unit for measuring the heating capacity of a heater. Watts are another unit for measuring power, and the two can be converted using a simple formula.
Conclusion
Determining the right heating capacity for your room size is crucial for achieving a comfortable and energy-efficient environment. By following the steps outlined above, you can confidently select the perfect heater for your needs. If you have any questions or need additional guidance, feel free to leave a comment or visit our website at https://cuahangxe.io.vn/ for more information about electrical and water products. We’re always happy to help!
Here’s a breakdown of the content, including EAVs, ERs, and Semantic Triples:
EAVs (Entity – Attribute – Value):
- Room – Size – 10×12 feet
- Room – Volume – 1200 cubic feet
- Room – Insulation – R-13
- Room – Window Area – 100 square feet
- Room – Ceiling Height – 8 feet
- Room – Occupants – 2
- Room – Climate Zone – 5
- Heater – Type – Space heater
- Heater – BTU – 15,000 BTU
- Heater – Watts – 4,400 Watts
- Heater – Efficiency – 90%
- Insulation – Type – Fiberglass
- Insulation – R-Value – 13
- Climate – Zone – 5
- Climate – Average Winter Temperature – 30°F
- Window – Material – Double-pane
- Window – Efficiency – 0.30
- Ceiling – Type – Standard
- Occupant – Number – 2
- Energy – Consumption – 1000 kWh/month
ERE (Entity, Relation, Entity):
- Room (Size) – Is Located In – House
- Room (Volume) – Requires – Heater (BTU)
- Heater (BTU) – Provides – Heating Capacity
- Heater (Type) – Is Used In – Room
- Insulation (R-Value) – Affects – Heat Loss
- Window (Area) – Contributes To – Heat Loss
- Ceiling (Height) – Influences – Heat Loss
- Occupant (Number) – Impacts – Heating Needs
- Climate (Zone) – Determines – Heating Capacity
- Heater (Efficiency) – Reduces – Energy Consumption
- Room (Size) – Requires – BTU Calculation
- Room (Volume) – Influences – Heating Capacity
- Room (Insulation) – Reduces – Heat Loss
- Room (Window Area) – Impacts – Heat Loss
- Room (Ceiling Height) – Affects – Heat Loss
- Room (Occupants) – Contributes To – Heating Needs
- Climate (Average Winter Temperature) – Influences – Heating Capacity
- Heater (Type) – Is Suitable For – Room (Size)
- Heater (BTU) – Is Needed For – Room (Volume)
- Room (Climate Zone) – Requires – Specific Heating Capacity
Semantic Triples (Subject, Predicate, Object):
- Room, has, Size
- Room, has, Volume
- Room, has, Insulation
- Room, has, Window Area
- Room, has, Ceiling Height
- Room, has, Occupants
- Room, located in, House
- Heater, provides, Heating Capacity
- Heater, consumes, Energy
- Heater, has, Efficiency
- Insulation, reduces, Heat Loss
- Window, contributes to, Heat Loss
- Ceiling, influences, Heat Loss
- Occupant, impacts, Heating Needs
- Climate, determines, Heating Capacity
- Climate, influences, Energy Consumption
- Room, requires, BTU Calculation
- Room, requires, Heater
- Room, needs, Specific Heating Capacity
- Heater, is suitable for, Room
